Electromechanical vs. Pneumatic Vibrators: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of industrial material handling, vibrators play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of various processes. Two primary types of vibrators dominate the market: electromechanical and pneumatic vibrators. Understanding the differences between these two options is essential for selecting the right equipment for your needs. This article delves into the features, advantages, and applications of electromechanical and pneumatic vibrators to help you make an informed decision. Electromechanical vs. Pneumatic Vibrators
What Are Vibrators?
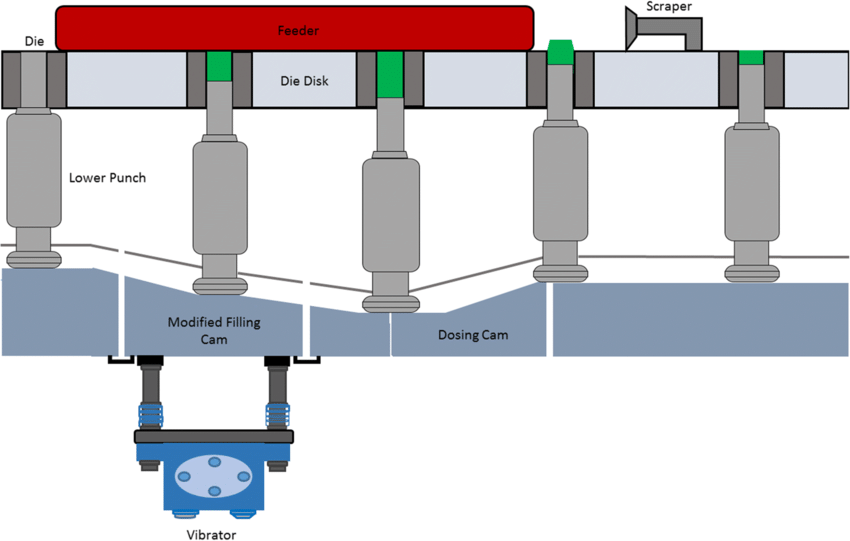
Vibrators are devices that create vibrations to facilitate the movement of bulk materials. They are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, mining, and construction to aid in the transportation and processing of materials. By generating controlled vibrations, these devices can effectively move, separate, and compact materials, ensuring efficient operations.
The Importance of Vibrators in Industrial Applications
Vibrators enhance productivity and efficiency in various industrial processes, including:
Material Handling: They help move bulk materials through chutes, hoppers, and conveyor systems.
Screening and Separation: Vibrators aid in the sorting and separation of materials based on size and density.
Compaction: They assist in compacting materials in storage bins or silos, reducing the risk of clogging.
With a clear understanding of vibrators’ importance, we can explore the two main types: electromechanical and pneumatic vibrators.
Electromechanical Vibrators
Electromechanical vibrators utilize electric motors to generate vibrations. They are known for their reliability, efficiency, and versatility, making them suitable for various applications.
Key Features of Electromechanical Vibrators
Power Source: Electromechanical vibrators are powered by electricity, which can be sourced from AC or DC power.
Design: They often feature a simple design with fewer moving parts, leading to lower maintenance requirements.
Adjustable Frequency: Many electromechanical vibrators allow users to adjust the frequency and amplitude of vibrations, providing flexibility for different applications.

Advantages of Electromechanical Vibrators
Efficiency: Electromechanical vibrators are energy-efficient, reducing operational costs.
Consistency: They provide consistent vibrations, ensuring uniform material flow.
Low Noise Levels: These vibrators generally operate quietly compared to pneumatic options, making them ideal for noise-sensitive environments.
Easy Installation: Electromechanical vibrators are straightforward to install and integrate into existing systems.
Applications of Electromechanical Vibrators
Electromechanical vibrators are widely used in various applications, including:
Hopper and Bin Discharge: They help facilitate the flow of materials from storage units.
Conveyor Systems: Used to maintain consistent material flow on conveyor belts.
Screening Machines: Electromechanical vibrators assist in the screening and sorting of materials in production lines.
Pneumatic Vibrators
Pneumatic vibrators operate using compressed air to create vibrations. They are commonly employed in environments where electricity may not be readily available or where explosion-proof operations are required.
Key Features of Pneumatic Vibrators
Power Source: Pneumatic vibrators rely on compressed air, making them suitable for specific industrial environments.
Compact Design: Many pneumatic vibrators have a compact design, allowing for easy installation in tight spaces.
Variable Vibration Settings: Users can adjust the airflow to control vibration intensity and frequency.
Advantages of Pneumatic Vibrators
High Power Output: Pneumatic vibrators can deliver high-intensity vibrations, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Versatility: They can be used in various environments, including those with hazardous materials.
Low Heat Generation: Pneumatic vibrators do not produce heat, reducing the risk of overheating in sensitive applications.
Explosion-Proof: Ideal for environments with flammable materials, pneumatic vibrators are less likely to cause sparks.
Applications of Pneumatic Vibrators
Pneumatic vibrators are frequently utilized in applications such as:
Foundries: Used for sand and material handling in casting processes.
Food Processing: Ideal for environments where cleanliness and hygiene are paramount.
Packaging Industries: Assists in the flow of materials during packaging operations.
Choosing Between Electromechanical and Pneumatic Vibrators
Selecting the right type of vibrator depends on various factors, including the application, environment, and specific requirements. Here are some considerations to help you decide:
1. Power Source
Consider whether you have access to electricity or need a device that operates on compressed air. If electricity is available and cost-effective, electromechanical vibrators may be the preferred choice. Conversely, if working in a hazardous environment or where electricity is limited, pneumatic vibrators may be more suitable.
2. Application Requirements
Evaluate the specific needs of your application. For high-intensity operations, pneumatic vibrators may provide the power needed. On the other hand, for applications requiring consistency and energy efficiency, electromechanical vibrators might be the better option.
3. Maintenance and Operational Costs
Consider the long-term operational costs, including maintenance and energy consumption. Electromechanical vibrators tend to have lower maintenance needs and operational costs due to their simple design and energy efficiency.
4. Noise Levels
If noise is a concern in your working environment, electromechanical vibrators are generally quieter and can help maintain a more pleasant working atmosphere.
Conclusion
Both electromechanical and pneumatic vibrators have unique advantages and applications in the industrial sector. Understanding their differences is essential for making an informed choice that aligns with your operational needs. By evaluating factors such as power source, application requirements, maintenance costs, and noise levels, you can select the best vibrator for your processes. This ensures efficient material handling and enhances productivity in your operations.